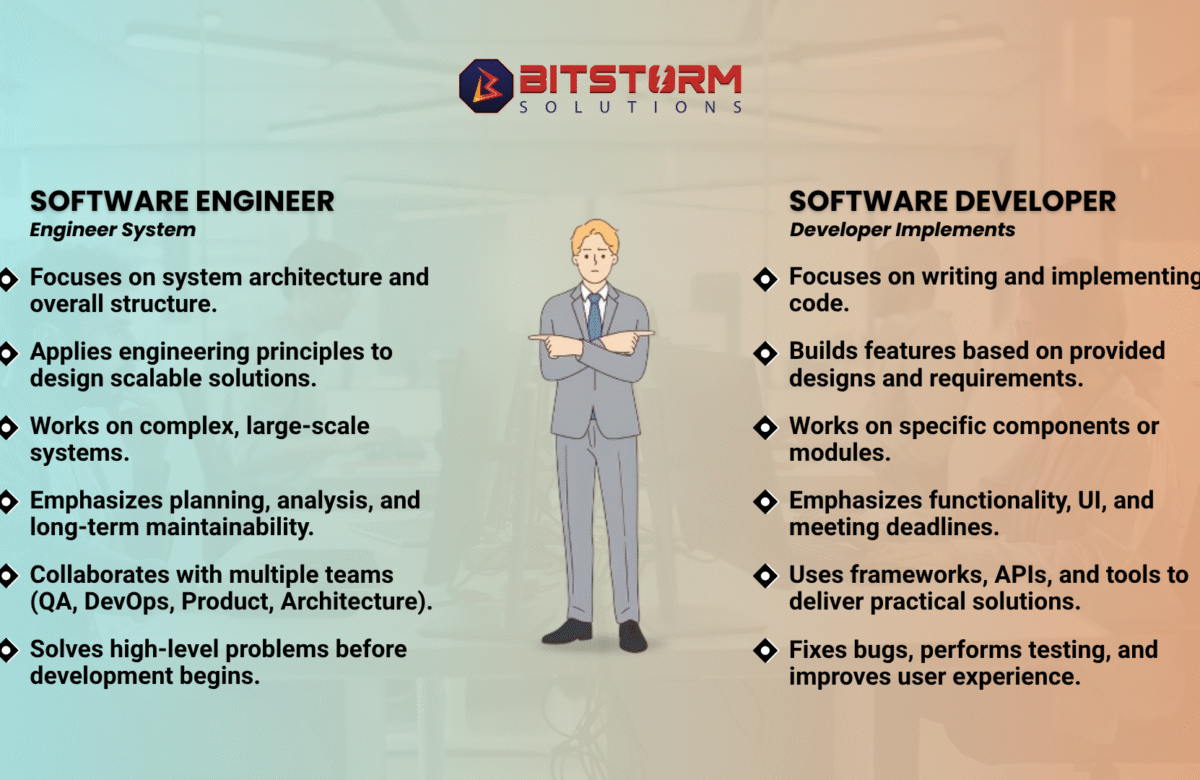
In an increasingly interconnected and complex digital landscape, the traditional castle-and-moat security model is no longer effective. Cyber threats are more sophisticated than ever, and breaches can originate from anywhere inside or outside your network. This is why Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has emerged not just as a buzzword, but as a critical strategic imperative for robust cybersecurity.
At Bitstorm Solutions, we believe that in the realm of digital security, trust is a liability. The core principle of Zero Trust is simple yet profound: “Trust No One, Verify Everything.” This fundamental shift in mindset moves away from implicit trust based on network location to explicit verification for every access attempt, every time.
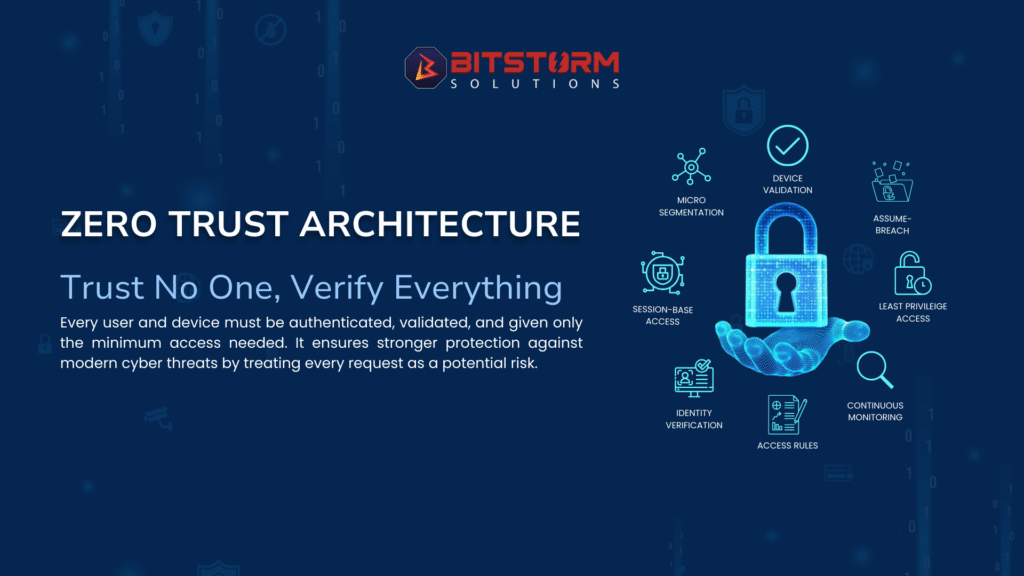
Let’s break down the foundational pillars of Zero Trust Architecture, as illustrated in our infographic:
1. Micro-segmentation:
Instead of a flat network, micro-segmentation divides your network into small, isolated zones. This significantly limits lateral movement for attackers, meaning if one segment is compromised, the damage is contained, preventing a widespread breach.
2. Device Validation:
Every device attempting to connect to your resources whether it’s a laptop, smartphone, or IoT device must be rigorously validated for its security posture, patch levels, and compliance before being granted access
3. Assume-Breach:
A core tenet of Zero Trust is to operate with the assumption that your network has already been, or will inevitably be, breached. This proactive mindset drives stronger security controls, continuous monitoring, and rapid response plans, focusing on detection and containment rather than just prevention.
4. Least Privilege Access (LPA):
Users and devices are granted only the minimum level of access required to perform their specific tasks, for the shortest possible duration. This drastically reduces the potential impact of compromised credentials.
5. Session-Based Access:
Access is not permanent. Instead, it is granted for a specific session, after which authentication and authorization must be re-established. This adds another layer of security, particularly for critical resources.
6. Identity Verification:
Strong, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is paramount. Every user’s identity must be continuously verified, not just at the point of login, but throughout their access session.
7. Access Rules:
Granular, context-aware access policies are defined and enforced. These rules consider various factors like user identity, device health, location, time of day, and the sensitivity of the resource being accessed.
8. Continuous Monitoring:
Zero Trust isn’t a one-time setup; it’s an ongoing process. All network traffic, user behavior, and system activities are continuously monitored for anomalies, suspicious patterns, and potential threats in real-time.
Why is Zero Trust More Critical Now Than Ever?
Remote Work Evolution: With distributed workforces, the traditional network perimeter has dissolved. ZTA secures access from any location.
Sophisticated Threats: Ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) demand a more dynamic and adaptive security posture.
Cloud Adoption: As organizations leverage hybrid and multi-cloud environments, Zero Trust provides consistent security policies across all platforms.
Regulatory Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks are increasingly aligning with Zero Trust principles, making it essential for compliance.
Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture is a journey, not a destination. It requires a strategic approach, careful planning, and the right expertise. Bitstorm Solutions specializes in helping organizations navigate this transformation, designing and deploying tailored Zero Trust frameworks that secure your digital assets and empower your business with confidence.